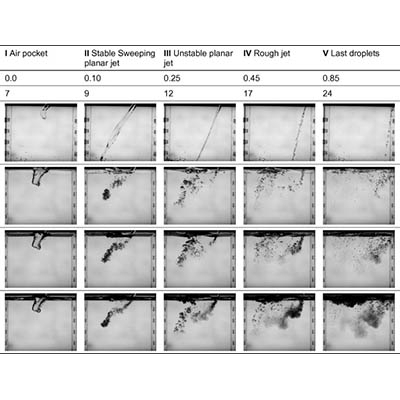
Quantification of the effect of oil layer thickness on entrainment of surface oil
This study quantifies the effect of oil layer thickness on entrainment and dispersion of oil into seawater, using a plunging jet with a camera system. In contrast to what is generally assumed, we revealed that for the low viscosity “surrogate MC252 oil” we used, entrainment rate is directly proportional to layer thickness. Furthermore, the volume of stably suspended small oil droplets increases with energy input (plunge height) and is mostly proportional to layer thickness. Oil pre-treated with dispersants (dispersant-oil ratio ranges from 1:50 to 1:300) is greatly entrained in such large amounts of small droplets that quantification was impossible with the camera system. Very low interfacial tension causes entrainment by even minor secondary surface disturbances. Our results indicate that the effect of oil layer thickness should be included in oil entrainment and dispersion modelling.